Status:
- 20231206 - The second revision of the PCB works and I tested with the whole satellite.
Known errors
- Through hole UART ✅
- The 5V converter doesnt work, change it for the TPS61023DRLT ✅
- It can be flashed and programmed via USB, change the USB to the ESP32, and put some jumpers to select where is going the USB✅
- QR code and revision and description
TESTS
Tests:
- Flash software and power led ✅
- Install i2c-tools and read simple registers ✅
- Execute the python script that reads the important registers ✅
- Get the reading of the NTC ✅
PRE-TESTS - Wiring with ESP-Prog
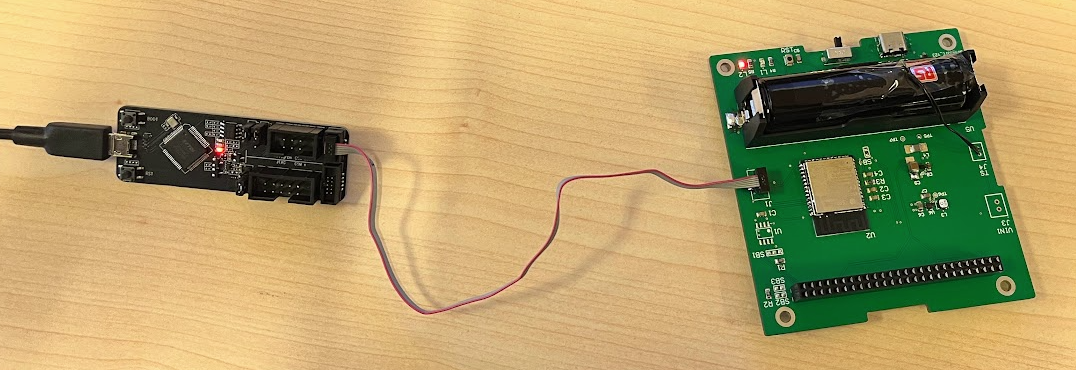
IMPORTANT The SPDT switch should be close to the USB-C connector.
PRE-TESTS - Wiring with usb connector
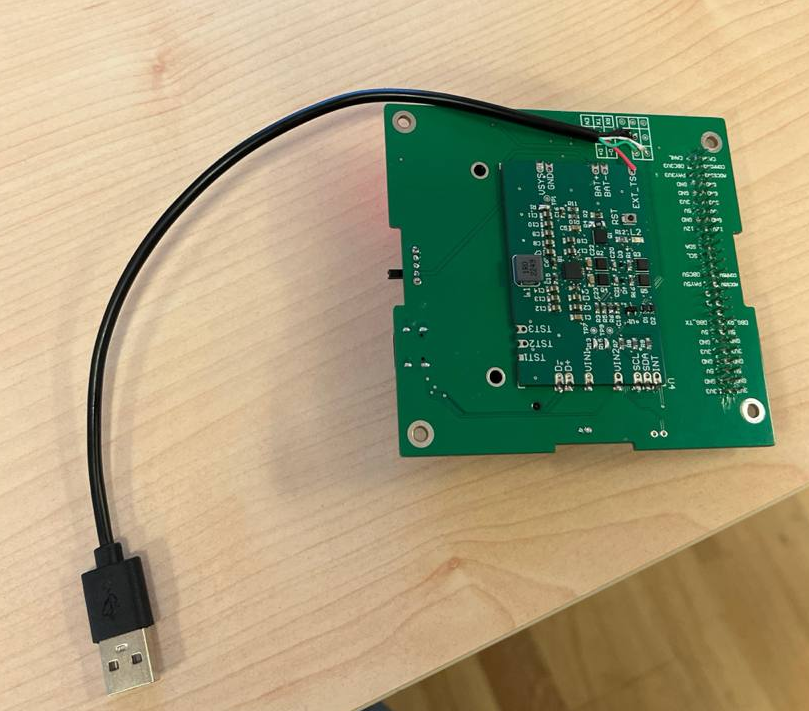

With this setup you can flash and debug, however there is a strange problem when you try to run esp i2c-tools.
TEST 1 - Flash and power led
You need to use arduino ide, select the second port, and the board is a ESP32S3-Dev Module. When you upload the code the led should be flashing.
// the setup function runs once when you press reset or power the board
void setup() {
// initialize digital pin LED_BUILTIN as an output.
pinMode(36, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
// the loop function runs over and over again forever
void loop() {
Serial.println("asdf");
digitalWrite(36, HIGH); // turn the LED on (HIGH is the voltage level)
delay(1000); // wait for a second
digitalWrite(36, LOW); // turn the LED off by making the voltage LOW
delay(1000); // wait for a second
}
TEST 2 - Install i2c-tools and read simple registers
The steps are
$ git clone https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf.git
$ cd esp-idf
$ git checkout a4afa44435ef4488d018399e1de50ad2ee964be8
$ . ./export.sh
$ cd examples/peripherals/i2c/i2c_tools
$ idf.py set-target esp32s3
$ idf.py -p /dev/serial/by-id/usb-FTDI_Dual_RS232-HS-if01-port0 flash monitor
And then inside you are in i2c-tools, a software to read the registers of the PMIC. To test that is working you can send a simple command and get a simple output:
i2c-tools> i2cget -c 0x6b -r 0x18
0x54
That means that is working :)
TEST 3 - Execute the python script that reads the important registers
You need to flash i2c-tools in the ESP32S3, like this way:
$ git clone https://github.com/espressif/esp-idf.git
$ cd esp-idf
$ git checkout a4afa44435ef4488d018399e1de50ad2ee964be8
$ . ./export.sh
$ cd examples/peripherals/i2c/i2c_tools
$ idf.py set-target esp32s3
$ idf.py -p /dev/serial/by-id/usb-FTDI_Dual_RS232-HS-if01-port0 flash
The you need to execute the next python script:
import serial
import time
# Open the serial port
ser = serial.Serial('/dev/serial/by-id/usb-FTDI_Dual_RS232-HS-if01-port0', 115200, timeout=1)
# BQ25798
chip_addr = "0x6B" # I2C device address
# Function to send an intro to the serial device
def send_intro():
intro = "\n" # Replace with your actual intro command
ser.write(intro.encode())
time.sleep(0.1) # Give it some time to process
ser.readline().decode().strip()
#print("Intro sent:", ser.readline().decode().strip()) # Print the response if needed
# Function to read the content of a specific register from the I2C device
def read_register(register_addr):
send_intro()
cmd = f"i2cget -c {chip_addr} -r {register_addr}\n" # Construct the command
ser.write(cmd.encode()) # Send the command over serial port
time.sleep(0.1) # Give it some time to execute and respond
ser.readline() # Discard the "i2c-tools>" prompt or echoed command
a = ser.readline().decode()
return a.strip() # Read and return the response
# Function to read and interpret the charger status from register 0x1C
def reg_charger_status_1():
value_hex = read_register("0x1C") # Read the value from register 0x1C
value_int = int(value_hex, 16) # Convert the hex value to an integer
charge_status = (value_int >> 5) & 0b111 # Extract bits 7-5
vbus_status = (value_int >> 1) & 0b1111 # Extract bits 4-1
print("Charge status: {}".format(charge_status))
print("VBUS status: {}".format(charge_status))
# Print the charge status
if charge_status == 0:
print("Charger Status: Not charging")
elif charge_status == 1:
print("Charger Status: 1 - Trickle charge")
elif charge_status == 2:
print("Charger Status: 2 - Pre-charge")
elif charge_status == 3:
print("Charger Status: 3 - Fast charge")
elif charge_status == 4:
print("Charger Status: 4 -Taper charge")
elif charge_status == 5:
print("Charger Status: 5 - Reserve")
elif charge_status == 6:
print("Charger Status: 6 - Top-off Timer active charging")
elif charge_status == 7:
print("Charger Status: 7 - Charge Termination Done")
else:
print("Charger Status: Unknown")
# Print the VBUS status
if vbus_status == 0:
print("VBUS Status: 0 - No input")
elif vbus_status == 1:
print("VBUS Status: 1 - USB SDP 500mA")
elif vbus_status == 2:
print("VBUS Status: 2 - USB CDP 1.5A")
elif vbus_status == 3:
print("VBUS Status: 3 - USB DCP 3.25A")
elif vbus_status == 4:
print("VBUS Status: 4 - Adjustable High Voltage 1.5A")
elif vbus_status == 5:
print("VBUS Status: 5 - Unknown (3A)")
elif vbus_status == 6:
print("VBUS Status: 6 - Non standard")
elif vbus_status == 11: # 0xB in decimal is 11
print("VBUS Status: 11 - Device directly powered from VBUS")
else:
print(f"VBUS Status: Unknown code {vbus_status}")
# Function to enable ADC by writing to register 0x2E
def enable_adc():
cmd = "i2cset -c 0x6B -r 0x2E 0xB0\n" # Construct the command
ser.write(cmd.encode()) # Send the command over the serial port
time.sleep(0.1) # Give it some time to execute and respond
ser.readline() # Discard the "i2c-tools>" prompt or echoed command
response = ser.readline().decode().strip() # Read the actual response
print("ADC enabled:", response) # Print the response
# Enable the Ibat discharge current sensing
def enable_ibat_sensing():
cmd = "i2cset -c 0x6B -r 0x14 0x3E\n" # Construct the command
ser.write(cmd.encode()) # Send the command over the serial port
time.sleep(0.1) # Give it some time to execute and respond
ser.readline() # Discard the "i2c-tools>" prompt or echoed command
response = ser.readline().decode().strip() # Read the actual response
print("ENABLE IBAT SENSING:", response) # Print the response
# Function to read and convert the battery voltage from register 0x3B
def reg_vbat_adc():
cmd = "i2cget -c 0x6B -r 0x3B -l 2\n" # Construct the command with length 2 bytes
ser.write(cmd.encode()) # Send the command over serial port
time.sleep(0.1) # Give it some time to execute and respond
ser.readline() # Discard the "i2c-tools>" prompt or echoed command
value_hex = ser.readline().decode().strip().split() # Read the response and split it into a list
parse_hex = int(value_hex[0], 16)*2**8 + int(value_hex[1], 16)
# Convert the hex value to an integer
#value_int = int(''.join(value_hex), 16)
# Convert the value to mV
battery_voltage_V = parse_hex * 0.001 # Each step is 1mV
print("VBAT: {} V".format(battery_voltage_V))
# Function to read IBUS ADC from register 0x31 and 0x32
def reg_ibus_adc():
cmd = "i2cget -c 0x6B -r 0x31 -l 2\n"
ser.write(cmd.encode())
time.sleep(0.1)
ser.readline() # Discard the prompt
value_hex = ser.readline().decode().strip().split()
parse_hex = int(value_hex[0], 16)*2**8 + int(value_hex[1], 16)
current_mA = parse_hex # Since it's current, directly assign the parsed hex value
print("IBUS: {} mA".format(current_mA))
# Function to read IBAT ADC from register 0x33 and 0x34
def reg_ibat_adc():
cmd = "i2cget -c 0x6B -r 0x33 -l 2\n"
ser.write(cmd.encode())
time.sleep(0.1)
ser.readline() # Discard the prompt
value_hex = ser.readline().decode().strip().split()
parse_hex = int(value_hex[0], 16)*2**8 + int(value_hex[1], 16)
# Handle two's complement for negative values
if parse_hex & (1 << (16 - 1)): # Check if the sign bit is set
parse_hex -= 1 << 16 # Compute negative value
current_mA = parse_hex
print("IBAT: {} mA".format(current_mA))
# Function to read VBUS ADC from register 0x35 and 0x36
def reg_vbus_adc():
cmd = "i2cget -c 0x6B -r 0x35 -l 2\n"
ser.write(cmd.encode())
time.sleep(0.1)
ser.readline() # Discard the prompt
value_hex = ser.readline().decode().strip().split()
parse_hex = int(value_hex[0], 16)*2**8 + int(value_hex[1], 16)
voltage_V = parse_hex * 0.001 # Convert to voltage
print("VBUS: {} V".format(voltage_V))
# Function to read VAC1 ADC from register 0x37 and 0x38
def reg_vac1_adc():
cmd = "i2cget -c 0x6B -r 0x37 -l 2\n"
ser.write(cmd.encode())
time.sleep(0.1)
ser.readline() # Discard the prompt
value_hex = ser.readline().decode().strip().split()
parse_hex = int(value_hex[0], 16)*2**8 + int(value_hex[1], 16)
voltage_V = parse_hex * 0.001 # Convert to voltage
print("VAC1: {} V".format(voltage_V))
# Function to read VAC2 ADC from register 0x39 and 0x3A
def reg_vac2_adc():
cmd = "i2cget -c 0x6B -r 0x39 -l 2\n"
ser.write(cmd.encode())
time.sleep(0.1)
ser.readline() # Discard the prompt
value_hex = ser.readline().decode().strip().split()
parse_hex = int(value_hex[0], 16)*2**8 + int(value_hex[1], 16)
voltage_V = parse_hex * 0.001 # Convert to voltage
print("VAC2: {} V".format(voltage_V))
# Function to read VSYS ADC from register 0x3D and 0x3E
def reg_vsys_adc():
cmd = "i2cget -c 0x6B -r 0x3D -l 2\n" # Construct the command with length 2 bytes
ser.write(cmd.encode()) # Send the command over the serial port
time.sleep(0.1) # Give it some time to execute and respond
ser.readline() # Discard the "i2c-tools>" prompt or echoed command
value_hex = ser.readline().decode().strip().split() # Read the response and split it into a list
parse_hex = int(value_hex[0], 16)*2**8 + int(value_hex[1], 16) # Parse the two bytes into an integer
# Convert the value to voltage (V)
vsys_voltage_V = parse_hex * 0.001 # Each step is 1mV
print("VSYS: {} V".format(vsys_voltage_V))
# Send an intro to the serial device
send_intro()
# Print the content of registers 0x1B, 0x1C, and 0x1D
#for reg in ["0x1B", "0x1C", "0x1D"]:
# value = read_register(reg)
# print(f"Content of register {reg}: {value}")
reg_charger_status_1()
enable_adc()
enable_ibat_sensing()
reg_vbat_adc()
reg_ibus_adc()
reg_vbus_adc()
reg_ibat_adc()
reg_vac1_adc()
reg_vac2_adc()
reg_vsys_adc()
send_intro()
And the output should be something like:
runfile('/home/facien/gitRepos/fauna/PMIC_BQ25798/read_registers.py', wdir='/home/facien/gitRepos/fauna/PMIC_BQ25798')
Charge status: 0
VBUS status: 0
Charger Status: Not charging
VBUS Status: 0 - No input
ADC enabled: I (23639) cmd_i2ctools: Write OK
ENABLE IBAT SENSING: I (23739) cmd_i2ctools: Write OK
VBAT: 4.134 V
IBUS: 2 mA
VBUS: 0.042 V
IBAT: -56 mA
VAC1: 0.0 V
VAC2: 0.004 V
VSYS: 4.134 V
TEST 4 - Get the reading of the NTC
import serial
import time
# Open the serial port
ser = serial.Serial('/dev/serial/by-id/usb-FTDI_Dual_RS232-HS-if01-port0', 115200, timeout=1)
# BQ25798
chip_addr = "0x6B" # I2C device address
# Function to send an intro to the serial device
def send_intro():
intro = "\n" # Replace with your actual intro command
ser.write(intro.encode())
time.sleep(0.1) # Give it some time to process
ser.readline().decode().strip()
#print("Intro sent:", ser.readline().decode().strip()) # Print the response if needed
# Function to read the content of a specific register from the I2C device
def read_register(register_addr):
send_intro()
cmd = f"i2cget -c {chip_addr} -r {register_addr}\n" # Construct the command
ser.write(cmd.encode()) # Send the command over serial port
time.sleep(0.1) # Give it some time to execute and respond
ser.readline() # Discard the "i2c-tools>" prompt or echoed command
a = ser.readline().decode()
return a.strip() # Read and return the response
# Function to enable ADC by writing to register 0x2E
def enable_adc():
cmd = "i2cset -c 0x6B -r 0x2E 0xB0\n" # Construct the command
ser.write(cmd.encode()) # Send the command over the serial port
time.sleep(0.1) # Give it some time to execute and respond
ser.readline() # Discard the "i2c-tools>" prompt or echoed command
response = ser.readline().decode().strip() # Read the actual response
print("ADC enabled:", response) # Print the response
# Enable the Ibat discharge current sensing
def enable_ibat_sensing():
cmd = "i2cset -c 0x6B -r 0x14 0x3E\n" # Construct the command
ser.write(cmd.encode()) # Send the command over the serial port
time.sleep(0.1) # Give it some time to execute and respond
ser.readline() # Discard the "i2c-tools>" prompt or echoed command
response = ser.readline().decode().strip() # Read the actual response
print("ENABLE IBAT SENSING:", response) # Print the response
def reg_ts_adc():
cmd = "i2cget -c 0x6B -r 0x3F -l 2\n" # Construct the command with length 2 bytes
ser.write(cmd.encode()) # Send the command over the serial port
time.sleep(0.1) # Give it some time to execute and respond
ser.readline() # Discard the "i2c-tools>" prompt or echoed command
value_hex = ser.readline().decode().strip().split() # Read the response and split it into a list
parse_hex = int(value_hex[0], 16)*2**8 + int(value_hex[1], 16) # Parse the two bytes into an integer
# Convert the value to voltage (V)
vsys_voltage_V = parse_hex * 0.0976563 # Each step is 1mV
print("TS: {} %".format(vsys_voltage_V))
# Send an intro to the serial device
send_intro()
enable_adc()
enable_ibat_sensing()
reg_ts_adc()
send_intro()
And the output is:
TS: 46.2890862 %
I put the hot air pointing to the NTC and the reading falls to 30%, in normal temperature is around 50%. It works perfectly.