I am running with a common problem that I find over the years in C, the C bit fields poacking.
The conclusion of making some tests are:
- Bit fields structures are for creating structures with the least memory possible
- Little endian and big endian is how the variables are saved into memory. In systems with different architecture this part will be sensitive.
- Fromt hese example we can see that is MSB firsts but the structures are sorted from the lower bit to higher. That is that version field in example 1 is at bits 0:2 in MSB, however from the CCSDS specification it is defined as bit 0 the first to be sent, however in this frame the first bit to be sent will be the bit 7, then 6 then 5 and so on. So the buffer represented is different in the example than with the CCSDS specification.
Be careful with HEX dump
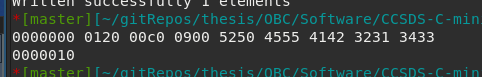
Be careful with hexdump. The first 4 digits is the first 2 bytes, where “01” is the second byte of the transmission and “20” is the first byte of the transmission.
Use the command xxd instead.
example 0
I am going to write about how data are packed on C.
struct t1 // 6 bytes
{
int a:12; // 0:11
int b:32; // 12:43
int c:4; // 44:47
}__attribute__((packed));
Example 1
- Version: 0b001
- type: 0b0
- sec_header_flag: 0b0
- proc_id: 0b00000000011
- seq_flags: 0b11
- seq_cnt: 0b0
- length: 0b110
typedef struct {
unsigned short version : 3;
unsigned short type : 1;
unsigned short sec_header_flag : 1;
unsigned short proc_id : 11;
unsigned short seq_flags : 2;
unsigned short seq_cnt : 14; //Seq count or packet name
unsigned short length;
} CCSDS_primary_header;
When printing is like:
76543210 and so on. The first bit represented is the bit 7, and the last of the octet is the 0.
01100001 00000000 00000011 00000000 00000110 00000000
Printing like:
void print_binary(unsigned char byte){
for (int i = 7; i >= 0; i--) {
printf("%d", (byte & (1 << i)) ? 1 : 0);
}
}
...
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
print_binary(ott[i]);
printf(" ");
}
How to extract the info
unsigned char buffer = 0b10111010; // assume buffer contains the byte you want to extract the parameters from
unsigned char version = (buffer >> 5) & 0b111; // extract the first 3 bits (bits 7-5) and mask the rest using bitwise AND operation
unsigned char type = (buffer >> 4) & 0b1; // extract the next 1 bit (bit 4) and mask the rest using bitwise AND operation
unsigned char flag = (buffer >> 3) & 0b1; // extract the next 1 bit (bit 3) and mask the rest using bitwise AND operation
unsigned char id = buffer & 0b111; // extract the last 3 bits (bits 2-0) and mask the rest using bitwise AND operation