Far field conditions
Rayleigh condition:
$$ r > \frac{2D^2}{\lambda} $$
Where D is the largest dimension of the antenna.
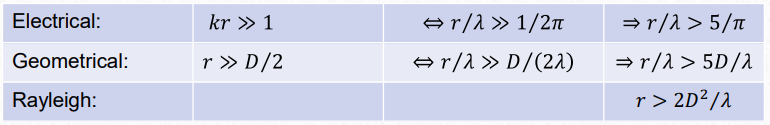
Compact ranges
In a compact ranges it is being modified the geometry of the wave with a reflector, to simulate a far field condition in which the waves a planar. In order to remove the edge diffracted rays it is used knife-edge or rolled-edge.
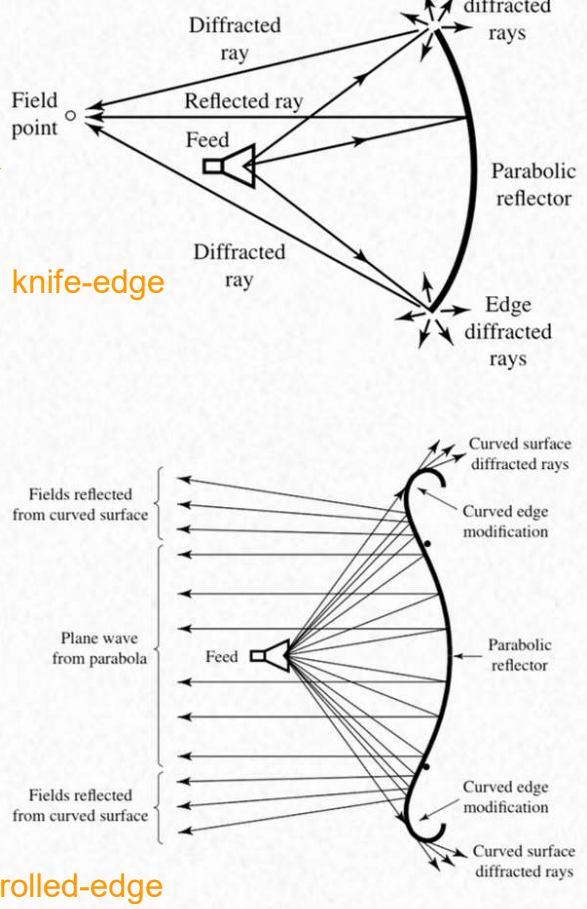
Near field measurements
It is considered electric small antenna when \(a « \lambda\), and electrically large antennas when \(D > 2.5 \lambda\).
- In reactive near field there is high mutual coupling, too close for accurate measurements
- Readiative Near-field: Is where the near-field measurements are done. Accurate farfield results after post-processing
There are three types of near field measurements:
- Planar
- Cylindrical
- Spherical
Near to far field
The steps are:
- Measure E(r) in a number of points on the spherical surface in the near-field region
- Calculate Q coefficients
- Calculate the E(r) in other r’s, in the far-field region.
$$ E(r) \approx \sum_{j=1}^{\infty} Q_j F_j(r) $$
Gain measurements
The measurements of gain are relative to the probe. In order to get the real gain of the antenna we need to use the next methods.
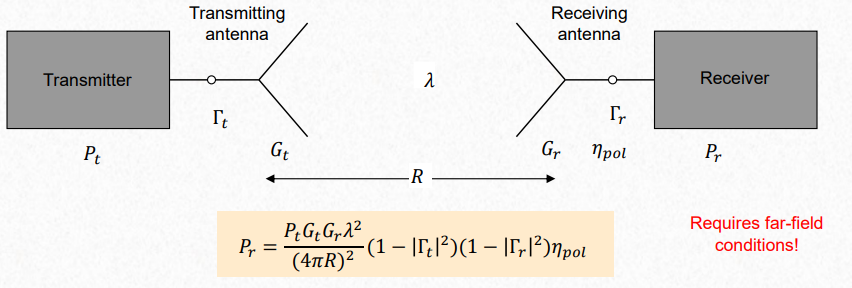
- Two antennas approach, to get the gain it is necessary that the gain is the same, impedance match.
- Three antennas approach, you suppose that there is impedance match, same R for all the antennas, same power. You get 3 incognitas with 3 powers.<